syndesmosis tear test|syndesmosis test : Brand High Ankle Sprain & Syndesmosis Injuries are traumatic injuries that affect the distal tibiofibular ligaments and most commonly occur due to sudden external rotation of the ankle. Diagnosis is suspected clinically with tenderness over the syndesmosis which worsens . WEBSe você fez um depósito na sua conta Betfair através de um cartão de débito, cartão de crédito ou carteira digital, você também terá que sacar fundos através deste mesmo .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 9 de jul. de 2021 · Game of Thrones- Season 4 (Music From The HBO Series).cue 1.84 KB 1891; Game Of Thrones.04.pdf 8.49 MB 8909600; .
syndesmosis widening
High Ankle Sprain & Syndesmosis Injuries are traumatic injuries that affect the distal tibiofibular ligaments and most commonly occur due to sudden external rotation of the ankle. Diagnosis is suspected clinically with tenderness over the syndesmosis which worsens .In surgery, you can test the stability of the syndesmosis. You can use the cotton .Pain reproduced with gentle force on the medial knee indicates a positive test. Palpation is helpful as a syndesmosis injury is typically tender at the anterolateral joint line and proximal .
Diagnosis can be difficult. Clinicians should consider the possibility of syndesmotic injury in athletes with pain or injury around the ankle or lower leg. Treatment too is different . The primary reasons for these discrepancies are that previous studies have failed to (1) properly distinguish between isolated (non-fractured) and non-isolated injuries, (2) .
you are analyzing a compound in the laboratory
According to Malhotra et al., a weight-bearing CT helps in the functional assessment of syndesmosis injuries; Diagnostic Ultrasound. Able to detect syndesmosis injury at ≥6.0 mm of tibiofibular clear space widening; MRI. .Key physical exam features include detailed documentation about areas of focal tenderness (syndesmosis and deltoid) and provocative maneuvers such as the external rotation stress .
In surgery, you can test the stability of the syndesmosis. You can use the cotton test, use a bone hook, or pull on the fibula by levering it out by hemostat, by a freer or an .Special tests for the evaluation of syndesmosis injuries include the squeeze test, the external rotation test, the fibula-translation test, the Cotton test, and the crossed-leg test. 18 Although a positive test should arouse suspicion to this .Pain with this test is considered a positive test for an ankle syndesmosis injury. The squeeze test itself has been shown to be highly sensitive and specific to diagnosing syndesmosis injuries. If you get a positive result with this test and the subjective assessment indicated a probable syndesmosis injury, then in most cases it is unnecessary .
Kleiger's test or external rotation is used for the diagnosis of a medial ankle sprain, to assess the deltoid ligament sprain and inferior tibiofibular syndesmotic sprain.. Technique [edit | edit source]. Patient position: in a seated position, .Taping used in the syndesmosis stabilization test. 64 Patients perform heel raises, walking, running, and vertical hopping (if possible) before and after 1.5-in. (3.8-cm) athletic tape is circumferentially applied over the tibiofibular syndesmosis to provide joint stability. The test result is positive if the patient’s complaints of pain and . Before you fix the syndesmosis, you will need to evaluate the reduction of the syndesmosis. This can be done by direct inspection and reduction or by x-rays. You may need x-rays of the other side to assess accuracy of reduction of the syndesmosis intraoperatively. In surgery, you can test the stability of the syndesmosis.Syndesmosis injuries are frequently overlooked and represent a cause for persistent pain in ankle sprains. Unstable syndesmotic lesions are always managed by surgery. . the anterior drawer sign is a standard test to identify ankle instability. . can detect latent diastasis in case of full syndesmosis tear but exhibit low reliability. 43,46 .
The Hook or Cotton test is more reliable than the exorotation stress test. The lateral view is more reliable than the AP mortise view because of the larger displacement in this direction. . The accuracy of AP radiography, mortise radiography and MRI was compared with arthroscopy for the diagnosis of a tear of the tibiofibular syndesmosis .
The first case of syndesmotic injury was described by Quenu in 1907 4 as a tibioperoneal diastasis after a ligamentous disruption and thereafter began to be studied in more depth. It has been classically described as being much less common than those of the lateral ligament, representing 1% to 18% of ligamentous lesions of the ankle. 5,6 However, recent .The squeeze test is also known as the fibular compression test and available literature suggests that it is used alongside with the ankle external rotation test. Technique [edit | edit source] The squeeze test compresses the proximal fibula against the tibia to assess the integrity of the bones, interosseus membrane, and syndesmotic ligaments .the external rotation test may be useful for diagnosing purely liga-mentous syndesmotic injuries. In thesqueezetest,1 compressionofthe fibula to the tibia above the mid-point of the calf causes separation of the two bones distally2 and pain at the area of the syndesmosis. In the external rotation test, pain over the syndesmosis is elicited with .syndesmosis tear Figure 1. Lateral ankle ligaments Reproduced from Brukner P, Kahn K. Clinical sports medicine, 3rd edn. Sydney: McGraw-Hill, 2007 . at the syndesmosis is regarded as a positive test Squeeze test With both hands clasp the medial and lateral aspects of the midcalf and squeeze. Pain distally at the site of
Conventional radiographs are usually the initial imaging test obtained after ankle injury. Widening of the ankle mortise and lateral shift of the talus with respect to the medial malleolus are radiographic signs of syndesmotic diastasis. . On the second image obtained inferior to the syndesmosis, a high grade partial tear of the anterior .High ankle sprains or syndesmotic ankle sprains are less common than other ankle pathologies. Athletes may experience it more frequently after forced external rotation and dorsiflexion of the foot. Injuries to the bones and ligaments of the ankle are associated with ankle syndesmosis injury. While surgical intervention is rarely indicated in the absence of fracture, conservative .Special tests for the evaluation of syndesmosis injuries include the squeeze test, the external rotation test, the fibula-translation test, the Cotton test, and the crossed-leg test. 18 Although a positive test should arouse suspicion to this injury, there are no studies demonstrating single test superiority at predicting syndesmosis injury or .
The syndesmotic ligament connects the two bones of the leg; this is often referred to as the ankle sydesmosis, or just syndesmosis.These bones, the tibia, and fibula are between the knee and ankle joints. The tibia is the larger shin bone that supports most of the weight of the body, and the fibula is the smaller bone on the outside of the leg. Sprained Ankles and Syndesmosis Injuries. Sprained ankles, including syndesmosis injuries, are among the most common issues we encounter. These injuries can range from mild ligament stretches to severe .
syndesmosis test
syndesmosis leg
Tenderness on palpation of the syndesmosis ligaments is the most sensitive test while the squeeze test is the most specific (Sman et al., 2015). Both being positive results in a high probability of injury to the syndesmosis ligaments. In .
A positive test result occurs when the patient has pain over the syndesmosis. The external rotation test has a sensitivity of 20% and a specificity of 84.8 . Increased translation relative to the contralateral side and pain indicates a positive test result. The ligament tear causes abnormal motion revealing excessively anteroposterior . Mild syndesmosis sprains usually involve a stretch or slight tear in only one of the ligaments making up the syndesmosis. Moderate tears of the ankle syndesmosis may lead to ankle joint instability, which make the ankle mortise loose. . Pain with this test is a hallmark of a syndesmosis injury. Tenderness can usually be pinpointed over the . test to identify a syndesmosis injury include. external rotation test. squeeze test. Imaging. . forward shift of more than 8 mm on a lateral radiograph is considered diagnostic for an ATFL tear. Imaging. stress radiographs. more accurate in chronic injuries. MRI. can diagnose injury. arthroscopic findings. can confirm MRI imaging. Background Non-invasive diagnosis of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis instability (DTSI) was a great challenge to clinicians. We designed a new method, the Standing on single foot-Binding test, and investigated the accuracy of the test in the diagnosis of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis instability in adults with a history of ankle injury. Methods 85 participants with .
In the squeeze test, pain is elicited over the ankle joint as the distal tibia and fibula separate when the leg is compressed at or slightly above mid-calf level. . Takao M, Ochi M, Oae K. Diagnosis of a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. The role of arthroscopy of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85-B:324–329. doi: 10.1302 .The squeeze test is performed by squeezing the leg just below the knee to see if pain radiates to the ankle area, which would suggest a high ankle sprain. With the external rotation test, your surgeon will bend your knee and place your ankle in neutral or 90 degrees with the foot in relation to the leg, and the foot is turned to the outside.
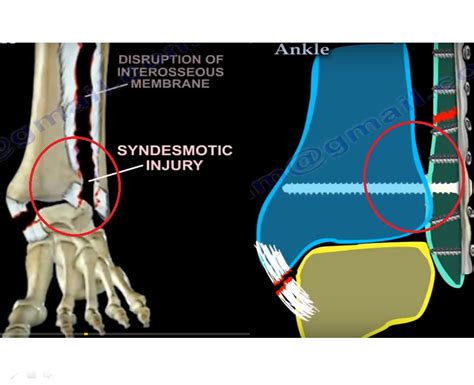
Prior studies have documented the ability of MRI to visualize the ligaments of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis [12, 13]; for the diagnosis of an anterior tibiofibular rupture, MRI has a sensitivity that ranges from 93% to 100%, with a specificity of 96–100% [].These figures showing high accuracy of MRI for diagnosis have been corroborated by others who report a 100% sensitivity . Anatomy of the syndesmosis. The tibiofibular syndesmosis is a fibrous joint joining the fibula to the tibia and stabilized by four lateral ligaments: the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL), the interosseous ligament (IOL), the transverse ligament (TL), and the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL) (Fig. 1).At the base of the syndesmosis, there is a small .
A translation of more than 4-5 mm on the injured would indicate a tear of ATFL. 2. Talar tilt test . A positive drawer test done 5 days after the injury, has been shown to be more sensitive and specific than the test done withing the 24-48 hours. 3. A sensitivity of 52% has been reported in a single study for the inversion talar tilt test. MRI has been shown to accurately detect injuries to the ligamentous structures of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis 1-3. The anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament is the one most often involved in such injuries and the most convenient to identify 2. Direct signs of a ligamentous tear include 2,4: abnormal course of the ligament
For this reason, an intraoperative syndesmosis-test-tool (STT) was developed and compared to the recommended and established hook-test (HT). Tests were performed on cadaveric lower legs (n = 20 .
hemoglobin content is assessed in the laboratory by analyzing:
O iToken app Itaú do computador autentica suas transações .
syndesmosis tear test|syndesmosis test